
Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts. In effect, companies are prevented from overstating net realizable value the value of their inventory, which reduces the risk of misleading investors. In this blog, we will explain the concept of NRV, how to calculate it, and provide examples to illustrate its application.
Understanding Net Realizable Value
If the loss is material, you may want to segregate it in a separate loss account, so that management can more easily spot these losses. The formula of NRV is the market value minus production and preparation costs. Companies’ profits depend on lenders and creditors and their liquidity to borrow money. With Correct NRV estimates the losses and gains for the upcoming future and prevents further damage from overstating assets.
Understanding Net Realizable Value (NRV)

GAAP rules previously required accountants to use the lower of cost or market (LCM) method to value inventory on the balance sheet. If the market price of inventory fell below the historical cost, the principle of conservatism required accountants to use the market price to value inventory. Market price was defined as the lower of either replacement cost or NRV. The expected selling price is calculated as the number of units produced multiplied by the unit selling price. This is often reduced by product returns or other items that may reduce gross revenue. It can also simply be done for just a single item rather than a group of units.

Formula and Calculation of Net Realizable Value
Once curtailed down, the inventory account becomes the new basis for reporting purposes and valuation. NRV is also used to account for costs when two products are produced together in a joint costing system until the products reach a split-off point. Each product is then produced separately after the split-off point, and NRV is used to allocate previous joint costs to each of the products. As part of this filing, Volkswagen disclosed the nature of the calculation of its inventory.
Accounts Receivable
Net realizable value is a critical concept in accounting, used to ensure that the value of assets on financial statements is not overstated. Here, we explore the application of NRV in different accounting contexts, including inventory valuation, accounts receivable, and cost accounting. This helps businesses determine the net amount they can expect to receive from selling an asset after accounting for any additional costs involved in the sale. An accounts receivable balance is converted into cash when customers pay their outstanding invoices, but the balance must be adjusted down for clients who don’t make payments. NRV for accounts receivable is calculated as the full receivable balance less an allowance for doubtful accounts, which is the dollar amount of invoices that the company estimates to be bad debt. GAAP requires that certified public accountants (CPAs) apply the principle of conservatism to their accounting work.
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
The calculation for Net Realizable Value has a variety of methods to get an answer. No matter which method you use to find the NRV, the value you find must fit the conservative method of accounting reporting. If the net realizable value calculation results in a loss, then charge the loss to the cost of goods sold expense with a debit, and credit the inventory account to reduce the value of the inventory account.
- Two of the largest assets that a company may list on a balance sheet are accounts receivable and inventory.
- NRV is a valuation method used in both generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and international financial reporting standards (IFRS).
- Inventory valued at net realizable value is those assets in inventory that include the expected selling price minus the total production cost.
- To calculate a value for inventory assets, companies calculate raw materials, labor, and other direct costs.
- Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
- In short, it measures the liquid value of a receivable account or inventory.Net Realizable Calculations can help business owners determine how much new sales and revenue can be expected from their current assets.
- First, you’ll have to determine the expected selling price or the market value.
- NRV is particularly important for valuing inventory and accounts receivable.
- Her areas of expertise include accounting system and enterprise resource planning implementations, as well as accounting business process improvement and workflow design.
- ABC International has a green widget in inventory with a cost of $50.
- It is the gross amount of AR minus any payment for doubtful accounts.
- For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
TranZact is a complete digital automation partner for Indian SMEs that solves valuation issues, achieving the target sales every time. Even if the product is not trendy, various broad markets use products as substitutes or cheaper alternatives. Now if the market value of the product reduces in the coming year to 200rs, the NRV is 60 rs. So the company will have a 40 rs loss, which is the difference between cost and net realizable value. Let’s say Star Company Inc Is selling some of its inventory to Moon and Co. To properly report the sale, Star Company is determining the net realizable value for the inventory they’re selling.
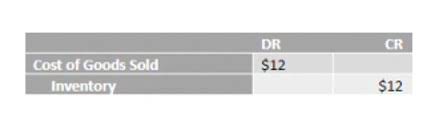
NRV is generally used on financial statements for assets that will be sold in the foreseeable future, not the ones expected to go up for liquidation. Now, let’s assume that a company’s inventory has a cost of $15,000. However, at the end of the accounting year the inventory can be sold for only $14,000 after it spends $2,000 for packaging, sales commissions, and shipping. Therefore, the net realizable value of the inventory is $12,000 (selling price of $14,000 minus $2,000 of costs to dispose of the goods). In that situation the inventory must be reported at the lower of 1) the cost of $15,000, or 2) the NRV of $12,000. In this situation, the inventory should be reported on the balance sheet at $12,000, and the income statement should report a loss of $3,000 due to the write-down of inventory.